SEO audit is a systematic health check of your website that identifies what’s working, what’s broken, and what’s costing you organic traffic. For growth-stage startups, a proper audit doesn’t just surface problems, it reveals the specific bottlenecks preventing you from scaling efficiently and lowering your customer acquisition cost. This 17-step framework gives you a complete roadmap to diagnose issues, prioritize fixes, and turn your website into a traffic-generating asset that performs in both traditional search and emerging AI-powered platforms.
A common mistake we see with most startups is that they waste months creating content without ever checking if Google can actually find it, if their site loads fast enough to keep visitors around, or if their technical foundation supports growth.
Let’s walk through the exact 17 steps that separate guesswork from data-driven SEO.
Table of Contents
What Is an SEO Audit?
“We’ve published 50+ blog posts and seen almost zero traffic, how do we figure out what’s wrong?”
The answer lives in a methodical audit.
An SEO audit is a comprehensive analysis of all factors affecting your website’s search engine visibility. Think of it as a diagnostic scan that examines three critical areas: technical infrastructure (can search engines access and understand your site?), content quality (does your site deserve to rank?), and authority signals (do other sites trust and link to you?).
Unlike vanity metrics that make you feel good without driving revenue, an audit focuses on actionable problems. It tells you why your best content isn’t ranking, why bounce rates are killing conversions, or why competitors with inferior products outrank you for high-intent keywords.
For startups operating with limited resources, audits prevent the expensive mistake of scaling broken systems. There’s no point doubling your content budget if technical errors prevent Google from indexing half your pages. You need to know exactly where you stand before you can plot the path forward.
What Tools Do You Need for an SEO Audit?
You don’t need a massive budget to run a professional-grade audit. Here’s the essential toolkit:
- Google Search Console (free) is non-negotiable. It shows you exactly how Google sees your site, including indexing issues, mobile usability problems, and Core Web Vitals performance. If you’re not using Search Console, you’re flying blind.
- Google Analytics 4 (free) reveals how visitors interact with your site, which pages convert, where users bounce, and which traffic sources deliver qualified leads versus tire-kickers.
- Screaming Frog SEO Spider (free up to 500 URLs, paid plans for larger sites) crawls your website like a search engine would, exposing broken links, redirect chains, duplicate content, and missing metadata that human eyes would never catch.
- PageSpeed Insights (free) measures your site’s loading speed and provides specific recommendations for improvement. Speed directly impacts both rankings and conversions.
For deeper competitive analysis and backlink research, consider Ahrefs or SEMrush (paid, but offer limited free trials). These platforms show you which keywords competitors rank for, who links to them, and where content gaps exist in your market.
AI monitoring tools are emerging rapidly. Platforms like Profound or custom ChatGPT queries can help you track how AI systems represent your brand, though this space is evolving quickly.
The key is using what you have access to rather than waiting for perfect tools. Google’s free suite alone can surface 80% of critical issues if you know where to look.
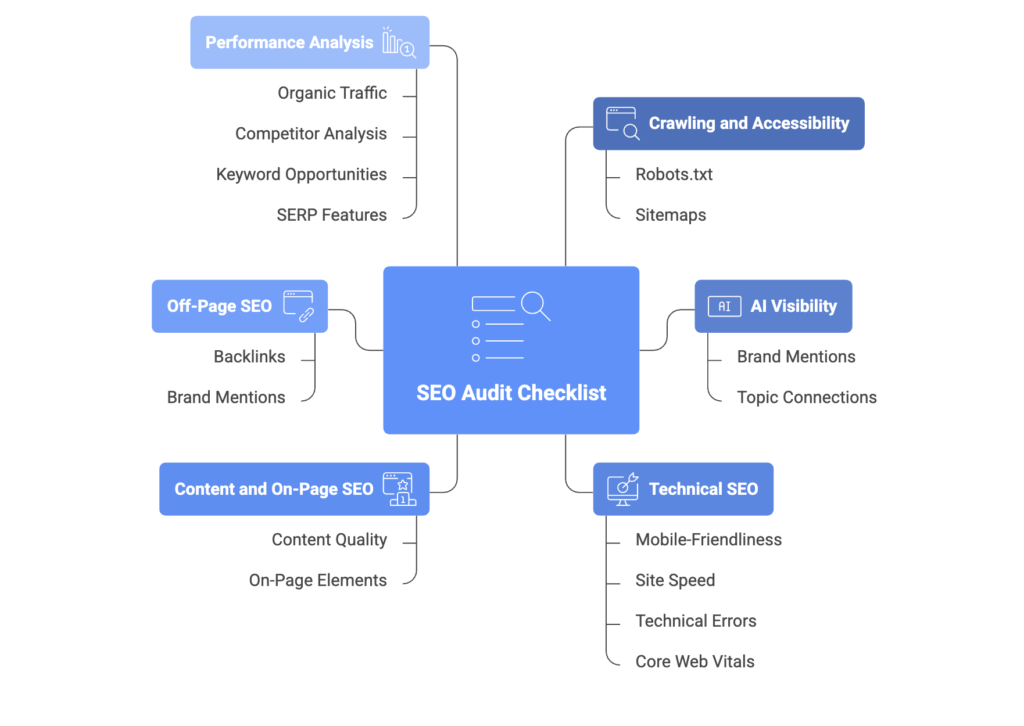
How to Do an SEO Audit: 17-Step Checklist
1. Make Sure Crawlers Can Access Your Site
Before anything else, verify that search engines can actually crawl your website. Check your robots.txt file (found at yoursite.com/robots.txt) to ensure you haven’t accidentally blocked important pages. A single misplaced line can hide your entire site from Google.
In Google Search Console, review the Coverage report under Index. Pages should appear as “Valid” rather than “Excluded” or “Error.” Common culprits include noindex tags left over from development, orphaned pages without internal links pointing to them, and server errors preventing access.
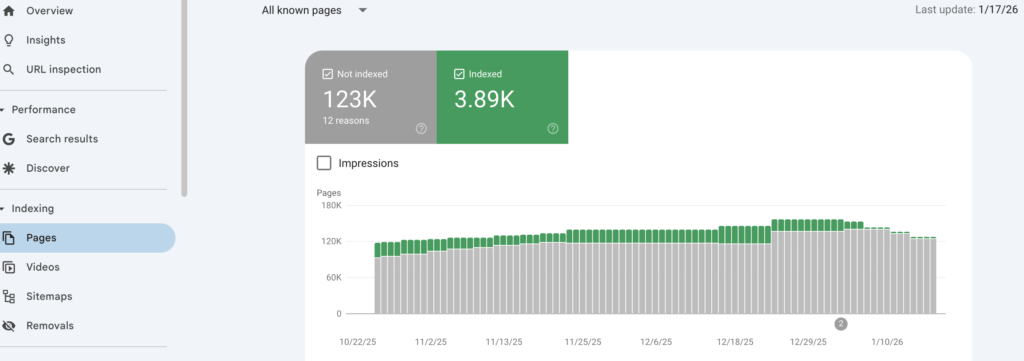
Test key pages using Google’s URL Inspection tool to see exactly what Google sees when it crawls. If Googlebot can’t access your content, nothing else in this audit matters.
2. Benchmark Your Current AI Visibility
AI-powered search through ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google’s AI Overviews represents a fundamental shift in how people discover information. You need to know where you currently stand.
Start by testing conversational queries your target customers might ask AI assistants. For example, if you sell project management software, try “What’s the best project management tool for remote teams?” or “How do I choose project management software for my startup?” in ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google.
Document whether your brand appears in responses, what context surrounds mentions, and whether competitors dominate the conversation. This baseline helps you track progress over time and identify which topics you need to strengthen.
You can use SevenSEO’s GEO audit tool and get detailed report in seconds.
3. See What AI Is Already Saying About Your Brand (and If It’s True)
Beyond broad queries, directly ask AI systems about your company. Search for “Tell me about [Your Company]” or “What does [Your Company] do?” across multiple platforms.
Record the responses. Is the information accurate? Is it outdated? Does it emphasize your strongest differentiators or focus on features you’ve since deprecated? AI systems train on publicly available content, which means old blog posts, outdated press releases, and competitor comparisons can shape how you’re represented.
If you discover inaccuracies, note them. You’ll address this by updating your most visible content, website pages, Wikipedia entries if applicable, major directory listings, to ensure accurate information dominates the training data.
4. Track Whether AI Connects Your Brand to Key Topics
This step reveals whether you own mindshare in your category. Test whether AI associates your brand with the topics that matter most to your business.
For instance, if you’re a growth marketing agency, query “Who are the leaders in growth marketing for startups?” If your brand doesn’t appear, you lack sufficient topical authority in AI knowledge bases.
Identify five to ten core topics central to your value proposition. Test variations of each query across platforms and track results. This isn’t about gaming AI systems, it’s about understanding whether your content strategy effectively communicates expertise in areas that drive business.
5. Check for Duplicate Versions of Your Site
Many sites accidentally create multiple versions that split their authority and confuse search engines. Check whether all these variations resolve to a single canonical version:
- http://yoursite.com
- https://yoursite.com
- http://www.yoursite.com
- https://www.yoursite.com
Pick one preferred version (typically https://www.yoursite.com or https://yoursite.com) and set up 301 redirects from all other versions. In Google Search Console, verify that only your preferred version is submitted as a property.
Also check for parameters creating duplicate content, things like session IDs, tracking codes, or sorting options that generate unique URLs for identical content. Use canonical tags to indicate the preferred version.
6. Ensure Your Site Is Mobile-Friendly
More than 60% of searches happen on mobile devices, and Google uses mobile-first indexing, it primarily evaluates your mobile site for ranking purposes.
Run your key pages through Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test. Look for issues like text too small to read without zooming, clickable elements positioned too close together, or horizontal scrolling caused by content wider than the screen.
In Search Console, review the Mobile Usability report for specific errors across your site. A poor mobile experience doesn’t just hurt rankings, it destroys conversions. A visitor who has to pinch-zoom to read your pricing page will abandon to a competitor before they ever see your value proposition.
7. Evaluate Your Site Speed
Page speed directly impacts both user experience and rankings. Run your homepage and top-performing pages through PageSpeed Insights or GTmetrix.
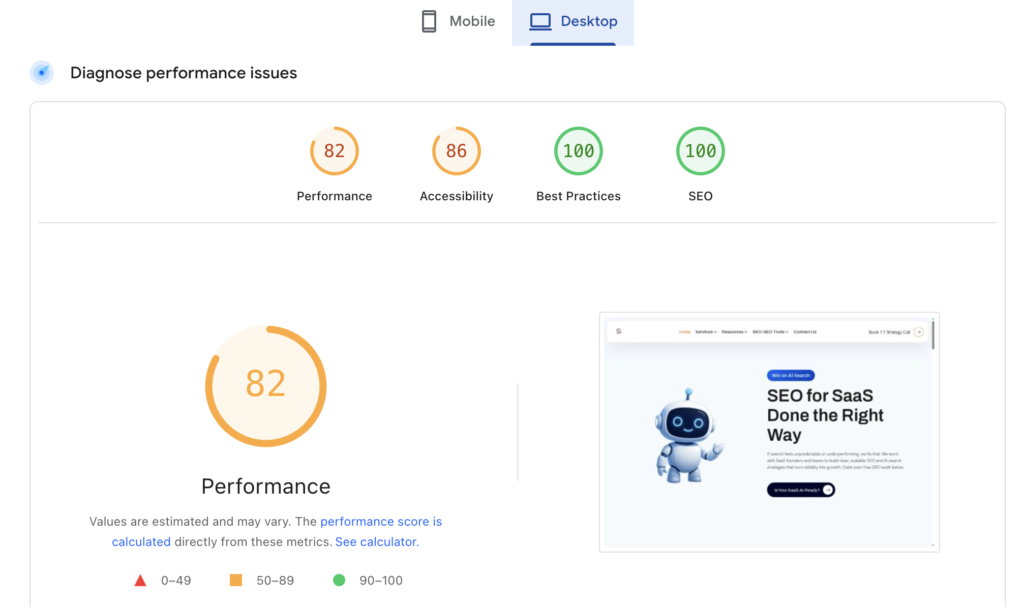
You’re looking for loading times under three seconds. Anything slower increases bounce rates exponentially. Common performance killers include oversized images, render-blocking JavaScript, lack of browser caching, and bloated CSS files.
PageSpeed Insights provides specific recommendations ranked by impact. Tackle the highest-impact fixes first, often compressing images and enabling caching deliver immediate improvements without requiring development resources.
For startups where every visitor counts, slow pages are revenue killers. Someone researching solutions won’t wait eight seconds for your comparison page to load when a competitor’s loads in two.
8. Crawl Your Site for Technical Errors
Launch Screaming Frog and crawl your entire site (or up to 500 pages on the free version). Export the data and filter for issues:
- Broken links (404 errors): Every dead link frustrates users and wastes crawl budget. Either restore the page or implement 301 redirects to relevant content.
- Redirect chains: Pages that redirect multiple times slow down crawlers and users. Redirect directly to the final destination in one hop.
- Missing or duplicate title tags and meta descriptions: These are fundamental on-page elements that should be unique for every important page.
- Large page sizes: Pages over 3MB will load slowly. Identify culprits, usually uncompressed images or video embeds, and optimize.
- Orphaned pages: Content with no internal links pointing to it essentially doesn’t exist. Either link to these pages from relevant content or remove them.
Create a spreadsheet categorizing errors by type and priority. Broken links affecting high-traffic pages should be fixed immediately; duplicate meta descriptions on low-traffic archive pages can wait.
9. Check Core Web Vitals
Core Web Vitals are Google’s standardized metrics for measuring user experience. They’re official ranking factors, which means poor scores directly hurt visibility.
In Search Console, navigate to the Core Web Vitals report. You’re evaluating three metrics:
- Largest Contentful Paint (LCP): Measures loading performance. Aim for under 2.5 seconds. This typically means optimizing server response times and ensuring your largest page element (often a hero image) loads quickly.
- First Input Delay (FID) / Interaction to Next Paint (INP): Measures interactivity. Users should be able to click and interact within 100 milliseconds. Long-running JavaScript usually causes problems here.
- Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS): Measures visual stability. Pages shouldn’t shift unexpectedly as they load. Reserve space for images and ads to prevent content from jumping around.
Pages marked “Poor” need immediate attention. Google provides specific affected URLs, focus on fixing your highest-traffic pages first for maximum impact.
10. Review Content Quality
Navigate to your top 20-30 pages by traffic in Google Analytics. For each, ask critical questions: Does this page answer the query that brings people here? Is the information current and accurate? Does it provide unique insights competitors don’t offer?
Look for content decay, pages that previously ranked well but have dropped. Often a refresh with updated data, new examples, or expanded sections restores rankings.
Identify thin content providing minimal value. A 200-word blog post stating obvious facts won’t rank and doesn’t deserve to. Either expand it significantly or delete it and implement a 301 redirect to more comprehensive content on the topic.
Check for keyword cannibalization, multiple pages competing for the same keyword. Consolidate these into one authoritative piece and redirect the others. You want one strong page per topic, not five weak ones fighting each other.
11. Check Your Site’s On-Page SEO
For every important page, verify these fundamentals are optimized:
Title tags should include primary keywords near the beginning and stay under 60 characters to avoid truncation in search results. They’re your headline make them compelling.
Meta descriptions won’t boost rankings directly but dramatically affect click-through rates. Summarize the page’s value proposition in 155 characters. Include a call to action when appropriate.
Header structure (H1, H2, H3) should create a logical hierarchy. Use one H1 per page containing your main keyword, H2s for major sections, and H3s for subsections. This helps both users and search engines understand content organization.
Image optimization: Every image should have descriptive alt text for accessibility and SEO context. File names should be descriptive (project-management-dashboard.png, not IMG_1234.png). Compress images to reduce file size without sacrificing visual quality.
Internal linking: Link from relevant content to your most important pages to distribute authority and help search engines understand site structure. Anchor text should be descriptive and natural, not generic “click here” phrases.
12. Analyze Your Brand Mentions and Backlinks
Backlinks remain a top-three ranking factor. Quality matters exponentially more than quantity, one link from an industry publication carries more weight than 100 links from low-quality directories.
Use Ahrefs, SEMrush, or the free version of Backlink Checker to audit your link profile. Identify your strongest links and analyze what made that content link-worthy. Look for toxic links from spam sites that could trigger penalties and disavow them through Search Console if necessary.
Also search for unlinked brand mentions instances where sites mention your company or product without linking. These represent easy backlink opportunities. Reach out politely asking if they’d consider linking to your site for readers wanting more information.
Track competitors’ backlink growth. If they land major placements, study what earned those links and create something even more valuable on the same topic.
13. Analyze Your Organic Traffic
In Google Analytics 4, filter for organic traffic and examine trends over the past 3-12 months. Look beyond vanity metrics like total visitors, focus on behavior.
Which landing pages convert visitors to leads or customers? Which pages have high traffic but terrible bounce rates, suggesting a mismatch between content and search intent?
Segment by device (mobile vs. desktop) and location if you serve specific geographic markets. Often you’ll discover mobile conversion rates lag desktop significantly, signaling usability issues.
Set up custom reports tracking your most important conversion paths. How many organic visitors view your pricing page? How many start free trials? Understanding these flows reveals where to optimize for business impact, not just traffic.
14. Benchmark SEO Performance Against Competitors
Identify your top three to five organic search competitors (not necessarily your business competitors—whoever ranks for keywords you want). Input their domains into Ahrefs or SEMrush alongside your own.
Compare domain authority, referring domains, and organic keyword rankings. This reveals how steep the climb is and where gaps exist.
Look at their content strategies. Do they publish comprehensive guides while you focus on short posts? Do they dominate video content or podcasts? Are they earning links from sources you haven’t considered?
This isn’t about copying competitors, it’s about understanding the competitive landscape and identifying opportunities they’ve missed or execution gaps in your own strategy.
15. Find Keywords You’re Missing Out on
Run a keyword gap analysis comparing your site to competitors. Tools like Ahrefs’ Content Gap feature or SEMrush’s Keyword Gap tool identify terms competitors rank for that you don’t.
Focus on keywords with commercial intent, phrases indicating readiness to buy rather than casual browsing. Terms like “best [product category] for [use case],” “[solution] pricing,” or “[competitor] alternative” signal high purchase intent.
Also identify questions your target audience asks. Tools like AnswerThePublic or Reddit searches in relevant subreddits (r/marketing, r/startups, r/Entrepreneur) reveal real language people use and pain points they express.
Create a prioritized list of keyword opportunities based on search volume, difficulty, and business relevance. Don’t chase high-volume vanity terms if they won’t convert to customers.
16. Find Missing Backlink Opportunities
Beyond analyzing your current backlinks, identify systematic opportunities you haven’t tapped. Look for:
Competitor backlinks: If a site links to three competitors but not to you, they’re clearly open to linking to companies in your space. Analyze what earned those links and pitch something similar or superior.
Resource pages and directories: Industry-specific directories, educational resource pages, and “best tools” roundups offer straightforward link opportunities if you qualify.
Broken link building: Find broken links on relevant websites, create content covering that topic, and suggest your page as a replacement.
Digital PR: Analyze which journalists and publications cover your industry. Build relationships by providing expert commentary, original data, or case studies they can reference.
Guest posting: Identify publications your target audience reads and pitch original insights they haven’t covered. Focus on value for their readers, not self-promotion.
Create an outreach plan with specific targets, personalized pitches, and a follow-up schedule. One quality backlink per week compounds dramatically over quarters and years.
17. Check Your Presence in SERP Features
Search results now include featured snippets, People Also Ask boxes, image packs, video carousels, and local packs. These SERP features often appear above traditional organic results, capturing significant click share.
Search for your target keywords and note which SERP features appear. Screenshot competitors who own these features and analyze their content structure. Featured snippets typically pull from content that directly answers questions in concise formats, paragraphs, lists, or tables.
Optimize your content to target these features. Use clear question-and-answer formatting, implement FAQ schema markup, create comparison tables, and structure how-to content with numbered steps.
Track your SERP feature presence in SEMrush or Ahrefs. Winning just a few high-volume featured snippets can deliver traffic equivalent to dozens of traditional rankings.
Putting Your SEO Audit Into Action
You’ve now identified dozens or hundreds of issues ranging from critical technical problems to strategic content gaps. Trying to tackle everything simultaneously guarantees you’ll fix nothing effectively.
Prioritize ruthlessly based on impact and effort. Create three buckets:
- Quick wins (high impact, low effort): Broken links on high-traffic pages, missing title tags, image compression, fixing mobile usability errors flagged in Search Console. Knock these out in the first week.
- Strategic initiatives (high impact, high effort): Comprehensive content rewrites, site architecture reorganization, building a systematic link acquisition process, improving Core Web Vitals. Schedule these across quarters with clear ownership and deadlines.
- Backlog items (low impact): Duplicate meta descriptions on archive pages, minor schema markup additions, refreshing old low-traffic content. Address when you have bandwidth or delegate to junior team members.
Build a shared spreadsheet tracking each issue with columns for category, priority, owner, deadline, and status. Review progress weekly in team standups. Nothing kills momentum faster than auditing thoroughly but never executing.
Set up monitoring so you catch new issues immediately rather than waiting for the next quarterly audit. Configure Search Console alerts for critical errors and coverage issues. Set up rank tracking for your most important keywords. Schedule monthly reviews of Core Web Vitals and organic traffic trends.
The startups that win treat SEO as a continuous optimization system, not a one-time project. Your audit isn’t the finish line, it’s the foundation for systematic growth that compounds month over month. Every broken link you fix, every page you optimize, and every quality backlink you earn creates an asset that drives traffic and reduces your customer acquisition cost for years to come.
The difference between startups that scale efficiently and those that burn cash on ineffective marketing often comes down to this: they know exactly where they stand, they fix what’s broken before scaling what’s working, and they let data guide decisions instead of assumptions. Your complete audit gives you that clarity. Now execute.
